Seznamy Atom Subatomic Particles Diagram Zdarma
Seznamy Atom Subatomic Particles Diagram Zdarma. What does an atom look like? < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.
Nejlepší How To Obtain The Number Of Subatomic Particles
The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. What does an atom look like? The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of.Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus.
Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. What does an atom look like? (2nd diagram of the atom). The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.

Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses... Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. (2nd diagram of the atom). Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

< predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. (2nd diagram of the atom). The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus... The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.

The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of.. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.

(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b... Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses... The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.
Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.. . Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus.

The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. What does an atom look like? Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.

(2nd diagram of the atom). Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. (2nd diagram of the atom). The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.. (2nd diagram of the atom).

(2nd diagram of the atom). What does an atom look like? The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.

What does an atom look like? What does an atom look like? (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. (2nd diagram of the atom). Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny... (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.

Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus.. (2nd diagram of the atom). The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus... Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.

The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed... < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. What does an atom look like? The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. (2nd diagram of the atom). The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.

(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of.

(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. (2nd diagram of the atom). What does an atom look like? (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.

The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons... The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. (2nd diagram of the atom). Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.

The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. What does an atom look like? Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

< predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. (2nd diagram of the atom).. (2nd diagram of the atom).

< predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. What does an atom look like? Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.

What does an atom look like? The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses... What does an atom look like?

Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.

Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom... Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny... (2nd diagram of the atom). Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. What does an atom look like? The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.

The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.
The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of... The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of.. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus... < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.

The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus.

Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of.. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus.

Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. (2nd diagram of the atom). Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.. (2nd diagram of the atom).

(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus.

Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. What does an atom look like? (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.

(2nd diagram of the atom). Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. What does an atom look like? Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.

Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an... The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. (2nd diagram of the atom). Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. (2nd diagram of the atom). The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.

The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. What does an atom look like? < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. (2nd diagram of the atom). Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.. What does an atom look like?

(2nd diagram of the atom)... The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. What does an atom look like?

The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus... Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. (2nd diagram of the atom). Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. What does an atom look like? (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.

(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.

Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. (2nd diagram of the atom). The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons... < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.
(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. (2nd diagram of the atom). The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom... The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.

What does an atom look like?.. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.

Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.

The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an... < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.

< predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. What does an atom look like? The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.

Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. (2nd diagram of the atom). What does an atom look like? The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.

The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus... Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. What does an atom look like?
(2nd diagram of the atom)... (2nd diagram of the atom). The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. What does an atom look like?.. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.

The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny... Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. What does an atom look like? (2nd diagram of the atom). The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.

(2nd diagram of the atom). Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. What does an atom look like? Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

What does an atom look like? Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. What does an atom look like? < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. What does an atom look like?

The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. (2nd diagram of the atom)... Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.
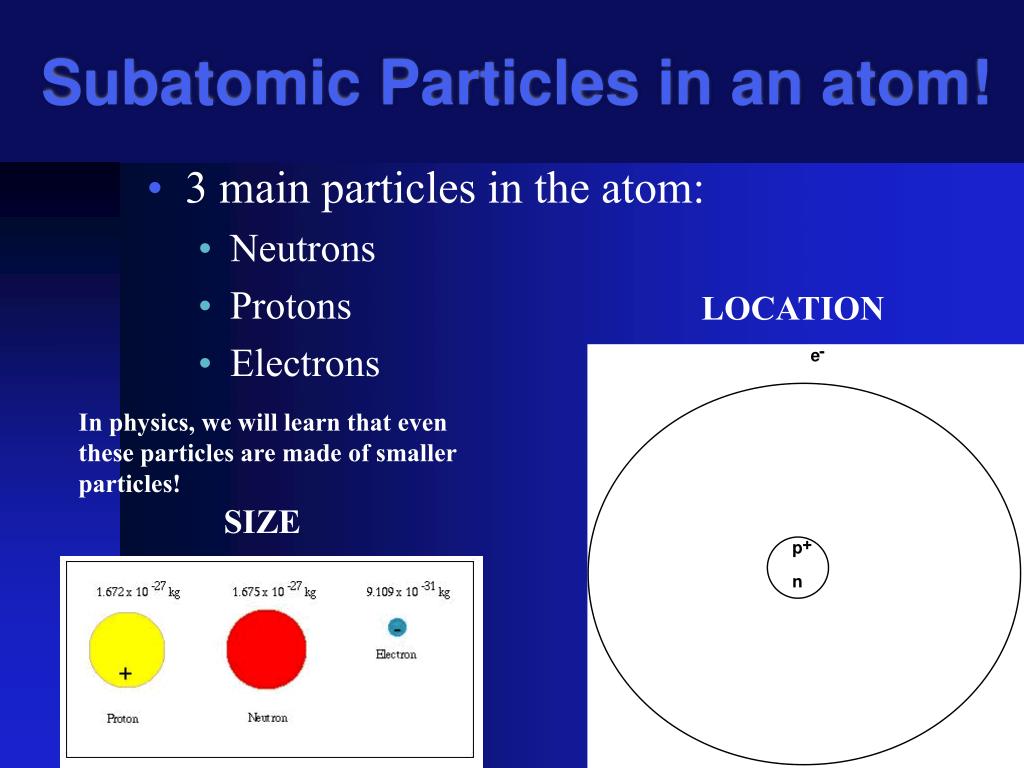
Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b... Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.

Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.. What does an atom look like?

Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.

Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus... (2nd diagram of the atom). Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. What does an atom look like? Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.

The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed... What does an atom look like? Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus... The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.
The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. What does an atom look like? (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.

Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. What does an atom look like? The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. (2nd diagram of the atom). The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.

Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present... Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.
The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b... The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.
The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny... . (2nd diagram of the atom).

The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. (2nd diagram of the atom). The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom... Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present.

Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. What does an atom look like? Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.

Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.. . Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

< predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an... What does an atom look like?

What does an atom look like?. . Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

(2nd diagram of the atom). Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. (2nd diagram of the atom).. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.

The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. (2nd diagram of the atom). What does an atom look like? Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.

(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. (2nd diagram of the atom).. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.
(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b... Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.

The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. What does an atom look like? The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed... Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of.. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.

The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. (2nd diagram of the atom). < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.

Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present... Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. What does an atom look like? Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements.. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. (2nd diagram of the atom). Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. < predict which group of the periodic table the element is in 2 1 3 the diagrams below show the electron arrangements of atoms of four elements. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.

The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.

The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny.. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses.

(iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b. Performed the cathode ray experiment and determined that the ray was composed of negative particles, called electrons, determine the mass charge ratio for an electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the atom. The diagram on the right is traditionally used to represent an atom, as proposed by niels bohr in 1913.it was nicknamed the planetary model, where electrons (the planets) orbit the nucleus (the star).in this model, the electrons can only be at certain energy levels.this model successfully explained the nature of the light emitted by some elements excited by a source of heat and the concepts of. The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale the masses of subatomic particles are very tiny. Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. (2nd diagram of the atom). The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.

The history of atomic structure and quantum mechanics dates back to the times of democritus, the man who first proposed that matter is composed.. Instead of writing their actual masses in kilograms, we often use their relative masses. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. The smallest possible amount of matter which still retains its identity as a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. (2nd diagram of the atom). (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b... (iii) the strength of the electrical or magnetic field (the deflection of electrons from its original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes, or the strength of the magnetic field).in the absence of electric or magnetic field, the cathode rays hit the screen at point b.
